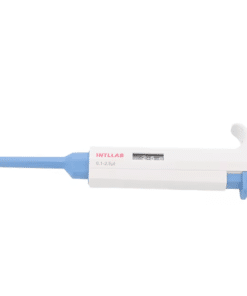
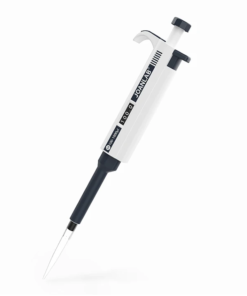
Micropipette
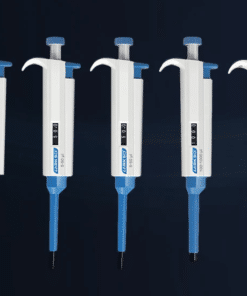
A micropipette is a laboratory instrument used to measure and transfer very small volumes of liquid, typically in microliters (µL). They are essential tools in various scientific fields, including biology, chemistry, and medicine.
Key components of a micropipette:
- Plunger: A button that controls the volume of liquid to be dispensed.
- Display: Shows the volume setting.
- Tip ejector: A button to eject the used pipette tip.
- Tip cone: Holds the disposable pipette tip.
Types of micropipettes:
- Single-channel micropipette: Can measure and dispense a single volume at a time.
- Multi-channel micropipette: Can measure and dispense multiple volumes simultaneously, often in rows or columns.
How to use a micropipette:
- Set the desired volume: Adjust the volume setting on the micropipette.
- Attach a pipette tip: Insert a disposable pipette tip onto the tip cone.
- Aspirate: Press the plunger to the first stop and immerse the tip into the liquid. Release the plunger slowly to draw the desired volume of liquid.
- Dispense: Place the tip against the target vessel and press the plunger to the first stop to dispense the liquid. To expel any remaining liquid, press the plunger to the second stop.
- Eject the tip: Press the tip ejector button to remove the used tip.
Key considerations when using a micropipette:
- Accuracy: Ensure proper technique to avoid errors in volume measurement.
- Precision: Use high-quality pipette tips and maintain the micropipette regularly.
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate the micropipette to maintain accuracy.
- Aseptic technique: Use sterile techniques to prevent contamination.
By mastering the use of micropipettes, scientists can perform precise and accurate experiments, leading to reliable results.
Micropipette
Micropipette
Micropipette
Micropipette
Micropipette
Micropipette