PH Meter
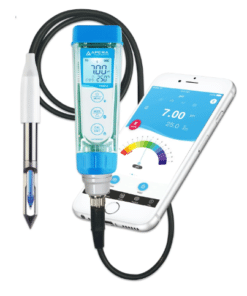
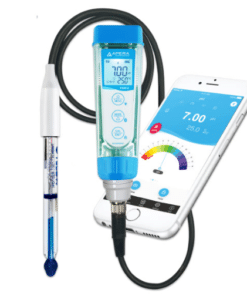
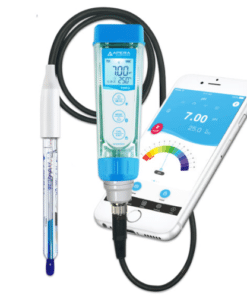
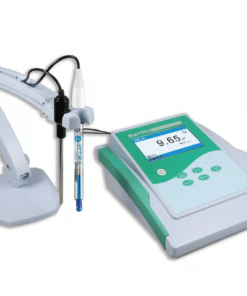
pH Meter
A pH meter is a scientific instrument used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It measures the hydrogen ion activity in a solution, which is expressed as a pH value.
How it works:
A pH meter typically consists of a pH electrode and a reference electrode. The pH electrode is a special type of electrode that responds to the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. When the electrode is immersed in a solution, a potential difference is generated between the pH electrode and the reference electrode. This potential difference is measured by the pH meter and converted into a pH value.
Key components of a pH meter:
- pH electrode: The sensing element that measures the hydrogen ion activity.
- Reference electrode: Provides a stable reference potential.
- Meter: Processes the electrical signal from the electrodes and displays the pH value.
Applications of pH meters:
- Laboratory research: Measuring the pH of solutions in various experiments.
- Environmental monitoring: Assessing the acidity of water bodies.
- Agriculture: Monitoring soil pH to optimize crop growth.
- Aquaculture: Maintaining optimal pH levels in fish tanks and ponds.
- Food and beverage industry: Controlling the pH of food and beverage products.
- Water treatment: Monitoring the pH of water during treatment processes.
Types of pH meters:
- Benchtop pH meters: Laboratory-grade instruments for precise measurements.
- Portable pH meters: Compact and portable for field use.
- Pen-type pH meters: Small and easy-to-use for quick measurements.
By understanding the principles of pH measurement and the applications of pH meters, you can effectively use this tool to monitor and control the acidity or alkalinity of various solutions.
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter
PH Meter